Italy’s Small Businesses Thrive Amid Economic Reforms
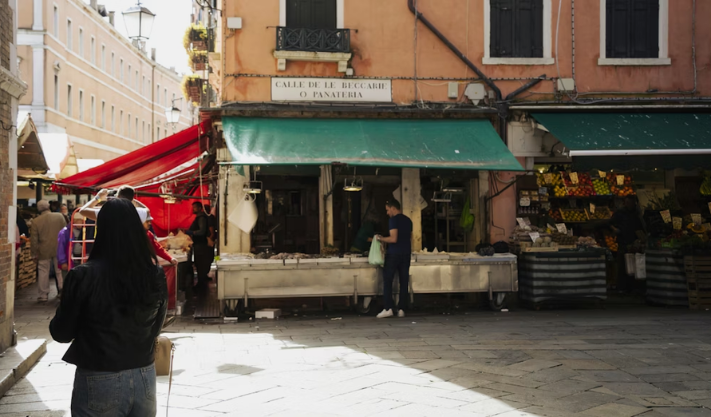
Italy, long celebrated for its rich history, culture, and artisanal craftsmanship, has historically faced economic challenges, from slow growth to bureaucratic hurdles. Yet, in recent years, the country’s small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)—which form the backbone of the Italian economy—are experiencing a renaissance. Strategic economic reforms, innovative entrepreneurship, and targeted government policies are driving renewed confidence and growth among Italy’s small business community.
The Backbone of Italy’s Economy
SMEs account for over 99% of Italian businesses and employ more than two-thirds of the workforce. They operate across diverse sectors, from fashion and food production to manufacturing and technology. Unlike multinational corporations, these smaller firms are deeply embedded in local communities, contributing not only to economic output but also to cultural identity and regional development.
Despite their importance, Italian SMEs have historically faced challenges such as complex tax systems, rigid labor laws, limited access to credit, and slow digital adoption. These hurdles often constrained growth and limited international competitiveness. However, a wave of reforms and market-driven innovation is changing the landscape.
Economic Reforms Fueling Growth
Since 2023, Italy has implemented a series of structural reforms aimed at supporting entrepreneurship and small business growth. Key measures include:
-
Tax Incentives and Simplification: New policies have reduced corporate tax burdens for small businesses and simplified compliance requirements, allowing entrepreneurs to reinvest savings into innovation and expansion.
-
Labor Market Flexibility: Reforms have introduced more adaptable employment contracts, making it easier for SMEs to hire skilled workers while maintaining operational flexibility.
-
Access to Finance: Government-backed credit schemes and loan guarantees have expanded financing options for smaller firms, particularly those looking to invest in technology or international expansion.
-
Digitalization Support: Grants and training programs encourage SMEs to adopt digital tools, from e-commerce platforms to advanced manufacturing software, improving efficiency and market reach.
These measures have lowered entry barriers for startups while enabling established small businesses to scale sustainably.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation Drive Success
Italy’s small businesses are leveraging their traditional strengths while embracing innovation. The country’s renowned craftsmanship, particularly in fashion, design, and food production, remains a competitive advantage. However, many SMEs are now integrating modern techniques, such as advanced manufacturing, AI-driven analytics, and digital marketing, to expand their reach domestically and abroad.
For instance, artisanal food producers in Emilia-Romagna are exporting locally made cheeses and pasta worldwide, supported by e-commerce and international logistics partnerships. Similarly, fashion ateliers in Milan are adopting virtual showrooms and online customization platforms, attracting global clients while maintaining their heritage branding.
Regional Variations and Opportunities
While economic reforms benefit SMEs nationwide, regional dynamics influence outcomes. Northern regions, including Lombardy and Veneto, historically have stronger industrial bases and infrastructure, giving local SMEs a competitive edge in manufacturing and exports. In southern Italy, reforms have been particularly impactful in stimulating entrepreneurship, as local governments and business associations provide training, financial incentives, and mentoring programs to foster new ventures.
Tourism-centric areas, such as Tuscany and Sicily, are also seeing small business growth, as firms adapt to changing travel patterns and consumer preferences. Boutique hotels, artisan workshops, and local food producers are capitalizing on the global demand for authentic cultural experiences, often combining traditional offerings with innovative marketing strategies.
Export and Internationalization
One of the most notable trends is the international expansion of Italian SMEs. Economic reforms have simplified export procedures and improved access to trade financing. As a result, small firms are reaching markets in North America, Asia, and the Middle East, showcasing products that combine quality, craftsmanship, and innovation.
Italy’s “Made in Italy” brand continues to be a powerful asset. Small businesses are emphasizing sustainability, ethical sourcing, and artisanal quality to differentiate themselves globally. This internationalization not only boosts revenues but also enhances competitiveness by exposing firms to global best practices.
Overcoming Persistent Challenges
Despite strong growth, Italian SMEs still face challenges. Access to talent remains a concern, particularly in technology-intensive sectors. Many small firms struggle to attract and retain young professionals with digital and managerial skills. Government initiatives promoting vocational training, apprenticeships, and university partnerships are beginning to address this gap.
Another hurdle is bureaucracy. While reforms have simplified some regulatory processes, administrative complexity can still slow business operations. SMEs often rely on business associations and local chambers of commerce for guidance, leveraging collective knowledge to navigate regulatory requirements efficiently.
The Role of Technology and Digital Transformation
Digital adoption is a major driver of SME growth in Italy. Small businesses are increasingly leveraging e-commerce, cloud computing, and digital marketing to expand their customer base. Manufacturing firms are embracing Industry 4.0 technologies, such as automation, AI-driven production optimization, and IoT-enabled monitoring, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Additionally, fintech solutions are streamlining payments, invoicing, and financial management. These tools empower SMEs to operate more competitively and efficiently, reducing reliance on traditional financial intermediaries.
Policy Support and Collaboration
Italy’s government, in partnership with European Union funding programs, continues to provide targeted support for SMEs. These include grants for research and development, incentives for sustainability initiatives, and mentoring programs for startups. Collaboration with industry associations, universities, and innovation hubs is fostering knowledge sharing and business networking, further strengthening small business resilience.
A Positive Outlook
Data from 2025 indicate that Italian SMEs are experiencing stronger growth than in previous decades, with rising revenues, increased employment, and expanding export activity. Confidence among small business owners is higher, reflecting optimism about long-term prospects. This momentum is critical for Italy’s broader economic recovery, as SMEs drive regional development, innovation, and social stability.
The combination of economic reforms, entrepreneurial innovation, and technology adoption is creating an ecosystem where small businesses can thrive. While challenges remain, the ability of SMEs to adapt and innovate demonstrates resilience and strategic vision.
Conclusion
Italy’s small businesses are proving that size does not limit impact. Through economic reforms, digital transformation, and global expansion, these enterprises are navigating a changing economic landscape with remarkable agility. By blending traditional strengths with modern strategies, Italian SMEs are not only surviving—they are thriving, setting a blueprint for sustainable growth in Europe and beyond.
As Italy continues to implement policies supporting entrepreneurship, innovation, and internationalization, its small business sector is poised to remain a powerful engine of economic growth, cultural pride, and global influence well into the future.
Also Read:
Can Europe’s Military Spending Boost Economic Growth?
Italy Lifestyle Businesses: How Innovation Drives Revenue
Europe’s Influencer Marketing Landscape: Key Insights for Brands